Effect of Nodulifying Agent in the Production of Nodular Cast Iron
Release time:
2024-08-05
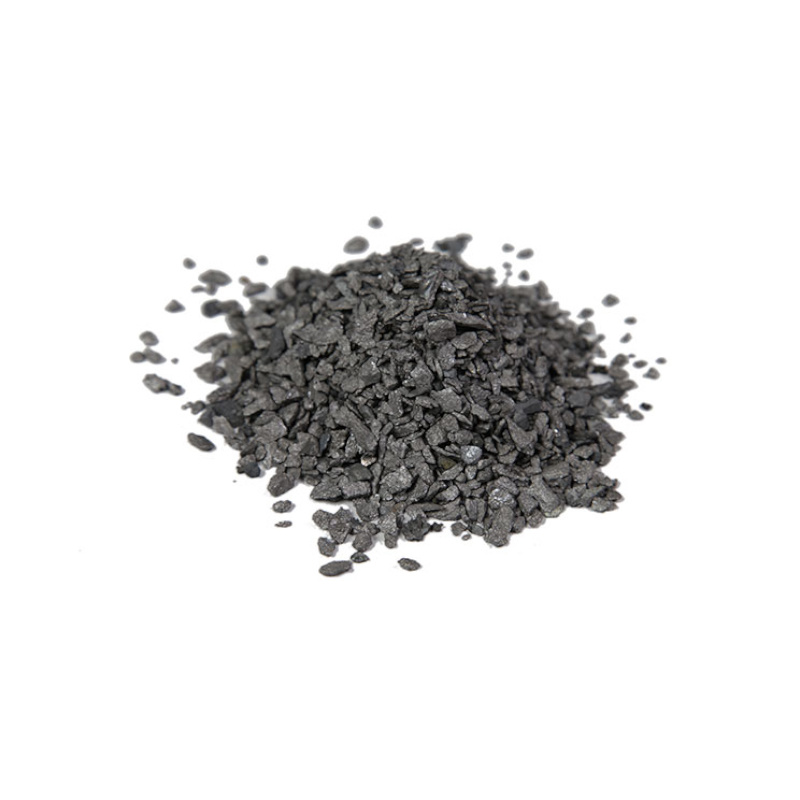
The spheroidizing element refers to an element that can promote the spheroidization of graphite and the generation or increase of graphite spheres.
The spheroidizing element refers to an element that can promote the spheroidization of graphite and the generation or increase of graphite spheres. The spheroidized elements generally have the following common properties:(1) There are one or two valence electrons in the outermost electron layer of the element, and 8 electrons in the second inner layer. This electronic structure makes the elements have a strong affinity with sulfur, oxygen and carbon, reflecting the stability of the product, which can significantly reduce the sulfur and oxygen in the water. (2) The solubility of elements in molten iron is low, and there is a significant tendency of segregation in the solidification process. (3) Although it has a certain affinity with carbon, it has low solubility in the graphite lattice. According to the above characteristics, Mg,Ce,Y,Ca are effective spheroidizing elements.
One is the high vapor pressure in the molten iron, so that the molten iron Buddha Teng. The atomic weight and density of magnesium is smaller than that of molten iron, with a melting point of 650 degrees and a boiling point of 1108 degrees. At the processing temperature of molten iron, the vapor pressure generated by magnesium is very high (over 1Mpa). The heat of fusion of magnesium is 21J/g and the latent heat of vaporization is 406J/g. Therefore, when magnesium is added to the molten iron, it is necessary to produce vaporization and make the molten iron churn. Two is with sulfur, oxygen has a strong affinity. The generated MgO and MgS have high melting point and density far less than iron, and are easy to separate from molten iron. Therefore, the contents of sulfur and sheep in molten iron after magnesium treatment are very low. Third, there is a tendency to segregate graphite during the solidification of molten iron. When the residual amount in molten iron exceeds 0.035, the powder can be spheroidized, but when the residual amount of magnesium exceeds 0.07, A part of magnesium is segregated in the grain boundary, and an exothermic reaction occurs in carbon, phosphorus, and the like in the grain boundary to generate MgC2, Mg2C3, Mg3P2, and the like. When the amount of residual magnesium is larger, the intergranular carbides increase.
Latest News